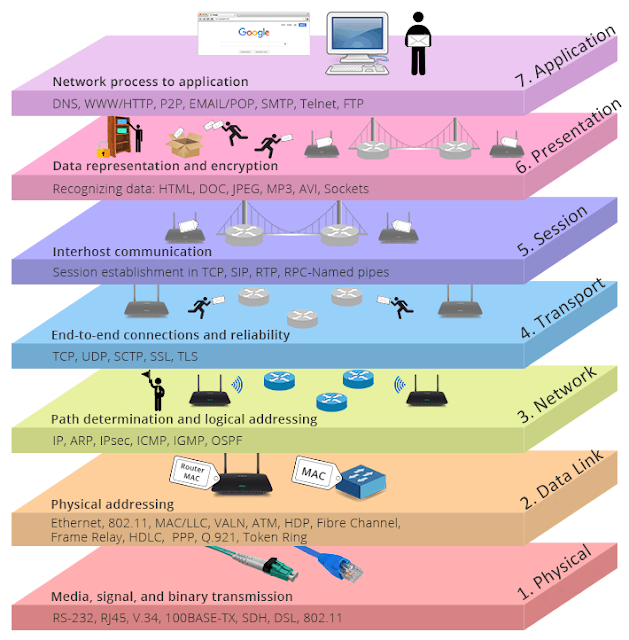
What is the OSI Model ?
Open system interconnection(OSI) model was developed by the International standard organisation ISO describe the flow of information from one computer to another.OSI model is also called ISO OSI reference model. It is a conceptual model that has seven layer. Physical layer, Data link layer, Network layer, Transport layer, Session layer, Presentation layer and Application layer. Each layer performs distinct function on the data in accordance with the previous layer function. The application present and session layers are called as upper layers.
All the layers of OSI reference model use different protocols. Protocols define the procedure that is to followed during data transmission. It is the set of specific rules and standard used to transmit data from one device to another device.
1. Physical Layer
Physical layer is the first or the bottom most layer of OSI model is used to establish a connection to a communication medium. It also define the electric electrical and mechanical specifications like cable connectors and signalling option of the medium.
Physical layer receive data from the upper layer called the data link layer it convert the data received data into bit stream the data is then transmitted through the medium to the receiver at the receiving end. Physical layer receives the data in bit format. It forward the data to the data link layer.
Physical layer receive data from the upper layer called the data link layer it convert the data received data into bit stream the data is then transmitted through the medium to the receiver at the receiving end. Physical layer receives the data in bit format. It forward the data to the data link layer.
Responsibilities of physical layer :-
Characteristics of media :
Define the characteristics of the interface which is used to connect in the devices it also defines the type of transmission media such as copper wire or Optical fibre cable.
Encoding :
Encoding defines the encoding type encoding is changing with streams (0s and 1s) into signals. Before transmission Physical layer encodes the signal into electrical or optical form depending upon the media.Transmission rate :
Transmission rates define the transmission rate of bits. This provides number of bits transmitted per second. It defines how long will the duration of a bit be.Transmission mode :-
Transmission mode defines the translation between two devices transmission mode specifies the direction of signal flow. The different type of Transmission mode is Simplex Half duplex and full duplex simplex communication is done only in one direction one device can only send and the other device only can receive, Half duplex communication is done in both directions but not at the same time, full duplex communication is done simultaneously in both direction at same time.Topology :-
It defines how the devices are connected to a form a network.2. Data link layer
Data Link Layer is the second layer of OSI model. It handles the data transfer between network and physical layer. Data unit at the data link layer is called as frame.Data link layer receive data from network layer. It adds header and trailer to this data and process data for the second layer at the receiver side. Data link layer receive data from the physical layer it detaches header and trailer from the data and process data to the network layer.Responsibilities of the data link layer
Framing :-
It delivers raw bit from the source to destination. During transmission the value of the bits can change. It is also possible that number of bits received by the receiver may be different from the number of bits send by the sender. To resolve this problem, The data link layer organised the bit into management data unit called as frames.Physical addressing :-
Physical addressing data link layer add header to the frame which contains the physical address of the sender and receiver header assignment the appearance are distributed to various system within the network.Error Control :-
Another function of these Data Link Layer is error control error control status and correct errors during transmission, if it is lost or corrupted, data link layer re-transmit that frame. it can also prevent duplication of frames. Error control is accomplished using trailer at the end of the frame.3. Network layer
This is the third layer of OSI model. The data unit is called in this layer is also known as packet. There is no need of the network layer if two communication devices lie on the same network. however, when the two devices are connected on different network, network layer is essential for providing source to destination delivery of packet.Network layer receive data from transport layer. It Adds header to the of data and passes data to the data link layer. At the receiver side network layer receives data from data link layer.
Responsibilities of network layer
Logical addressing :-
The data link layer provide physical addressing which is useful for a open network. When the packet is this destined for a device outside the network, We required for other address in c scheme to identify source and destination. Network layer adds header to the data that includes the logical (IP) address of the source and destination.It is a 32 bit address that uniquely identifies the devices connected to the network.
Routing :-
Routing is a process wherein a proper path is defined for the packets to reach the destination. Routing can be of two types, Static and dynamic .In the static routing the route to followed by a packet is already set by the network administrator. In dynamic routing , the route to be followed by a packet is decided at the time of transmission of the packet. The route can be changed based on the available traffic on the network.
Internetworking :-
Internetworking means connecting two or more computer network together. The internet is the best example of Internetworking. There are different types of networks that exist in the real world such as LAN, MAN and WAN. These network are interconnected using various networking devices such as bridges, routers and gateways.











0 Comments